Title: Samsung Internationalization
Category: Coursework
Sub Category: Global Business Management
Subject: International Business
References: APA
THE GLOBAL MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION: CASE OF SAMSUNG
1.0 COMPANY BACKGROUND:
According to Lee and Lee, (2004) Samsung Group is Korean based company operating in consumer electronics segment established in 1969. Samsung started up with the manufacturing of black and white television with joint venture with SANYO which Japanese consumer electronics manufacturer. Samsung started its mobile manufacturing in 1988 launching their first cell phone SH-100 for Korean market. Since then Samsung mobile phone segment has been an advocate of innovative design, functionality, performance and user friendly interface. Extensive R&D and investment in new wireless technology enabled Samsung to achieve its competitive advantage based upon the technology leadership, economies of scales, brand power, and superior negotiation power over suppliers and mobile service providers. In recent times Samsung has emerged as a largest conglomerate with more than 80 subsidiaries operating in diversified product division of construction, consumer electronics, financial services, shipbuilding, and medical services. Samsung has been emerged as top 10 fortune companies with revenue exceeding $100bn in 2007.
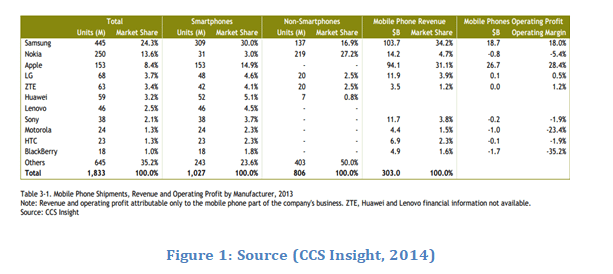
Samsung is a dominant player in Smart phones industry and emerged as a market leader and largest Smartphone manufacturer in the world surpassing Apple, Nokia and Sony. According to CSS, (2014) report global smart phone industry have change market dynamics of consumer electronics witnessing extraordinary growth in recent years with shipment exceeding 40% in 2013 reaching the threshold of 1 billion units and $266 billion in value. In 2013 two competitors Apple Inc and Samsung comprises of two third of industry revenue with duopoly market structure while facing intense market competition with IOS and Android interface. In context of market share of Smartphone and non-smartphones Samsung is leading the market with the total market share of 24.3% selling 445 million phones sets both smartphones and non-smartphone in 2014.

The below table shows the global market structure of Smart phone industry in context of market share and revenue
1.0 STAGES OF INTERNATIONALIZATION:
Globalization has created opportunities for firms to extend beyond the border of their home country and operate with affiliates and branches in more than one country. Firms are becoming multinational to exploit three opportunities which include ownership advantage, localization advantage and lastly internalize benefits of owning technology, brand or expertise. (Cotera and Ghauri, 2000) Literature on international business and managing multinationals suggests brief options of modes which firms might use to enter a foreign market which includes exports via company owned channels, contractual modes such as licensing and franchising or through FDI which includes joint venture and acquisitions.
1.1 Uppsala Model of Internationalization:
The internationalization process described in the Uppsala model shows how the firms gather experience in their home country before entering and investing in a foreign market. Phenomenon of internationalization of firms can be best explained using Uppsala internationalization model, which describes the phases, stages and strategy through which firms enter international markets. According to the U model firms initiate’s internationalization by direct exports then move towards in-direct exports, then later on establishes sales subsidiaries and lastly moving towards establishing production facility in the host country. However, it is not essential for companies to follow traditional model of internationalization as many companies have been witnessed to called global start-ups high technology start-ups and international new ventures. (Forsman, Hinttuand and Kock, 2012)
1.1 (a) Direct Exports:
The Samsung group is the biggest business conglomerate in South Korea and one of the world’s biggest multinational companies. Samsung grew with strong international orientation. The motivation for Samsung as a conglomerate was to seek for its survival to poor resource endowment in Korea. Samsung made its first foray into the global market in 1996, when it exported its PCS phones to Sprint, an American CDMA carrier. Sprint had been supplied with its PCS phones from Sony, but as it sought out more advanced phones, it realized that Samsung was one of only a few companies that offered such phones.9 Sprint signed a $600 million contract with Samsung, under which Samsung would provide its PCS phones to Sprint for three years under the cobranded name “Sprint-Samsung. After the success of CDMA phones in US markets, Samsung expanded its operation in Hong Kong in 1997 and 1998 Samsung entered Brazil with the strategy of direct exports. Samsung’s leading position in CDMA technology and its significant domestic market share gave it the confidence and momentum to go abroad. Samsung targeted countries that use the CDMA technology for mobile communication. In 1999, Samsung secured the number one position in the worldwide CDMA market where it accounted for more than 50% of market share. (Lee and Lee, 2007)By the advent of twenty first century financial crisis had a significant impact on most Korean large corporations. Expansion to foreign markets, especially Asian markets, was a means to compensate for contraction in the U.S. and European markets. Samsung Electronics increased its foreign assets by increasing the number of foreign affiliates and their size. (Porras and Aymes, 2010)
1.1 (b) Joint Venture:
Samsung entered the arena of global manufacturing via joint venture, which started up in China where primary motivation for global manufacturing of a Korean firm is to gain access to certain resources in a foreign country, including natural resources or human resources like inexpensive or professionals. In order to maximize benefits from economies of scale and scape Samsung has strategic alliance with Chinese firms which variety of inter-firm cooperation agreements ranging from shared research to formal joint venture and minority equity participation. By the advent of that time The GSM market accelerated Samsung’s growth, providing new opportunities. Samsung’s high-end positioning, along with its quality product, helped raise the prestige of Samsung’s mobile phones to that of a luxury good. Samsung strategic challenge was primarily potential profits from erosion through competition in international markets and bargaining power of customer supplier and government. The multinational strategic approach leads Samsung to depend on local-for-local innovations, a process requiring the subsidiary to not only identify local needs but also use its own local resources to respond to those needs (Bartlett et.al., 2008). Samsung have adopted a market-seeking mode of global manufacturing when it chooses to produce its goods near a target market to understand the customer’s needs and to adapt and tailor the product to respond to local demand changes. Only in South East Asia Samsung mobiles have 63 different units (13 manufacturing, 16 sales and 34branch and representative offices) in 16 countries. This shows the glimpse of multi domestic internationalization strategy used by Samsung. Samsung has continued to develop the expertise of its people in different regions. It strengthens its existing brands by promoting innovations throughout the market. Samsung telecom division expands its markets by developing a resilient, diversified portfolio of leading brands which can give the company a strong platform to deliver future growth.
1.1 (c) R&D Consortia:
According to Shannon and Manley, (2013) Research and development (R&D) consortia are formed by manufacturing companies, often with the support of government, for the purpose of conducting shared research on new technologies for the benefit of the consortium’s member companies. Innovation is crucial to Samsung’s business. As new technologies are being constantly introduced to the market, speed is essential for remaining competitive in today’s digital era, and new markets have to be pioneered continuously. Through the interplay of creative, imaginative people; a global R&D network; an organisation that encourages collaboration and cooperation among business partners all along the supply chain; and a strong commitment to ongoing investment, Samsung has put R&D at the heart of everything as it has 42 research facilities around the world collaborating on strategic technologies for the future and original technologies designed to forge new market trends and set new standards for excellence. Innovation is a global enterprise at Samsung as their research and development network spans six Samsung centres in Korea and 18 more in nine other countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Russia, Israel, India, Japan and China, as well as other research centres and universities. Closely linked, these centres are tasked with hiring top-notch local talent, investigating the latest local technology trends, and bringing to life those technologies that offer the greatest benefits. (Official Samsung website, 2014)
[Get Premier Coursework Writing Help From Expert Writers & Boost Your Academic Performance ]
2.0 INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL TRIGGERS TO EACH IDENTIFIED STAGE:
2.1 Internal and External Triggers at “Direct imports” Stage:
At direct export stage of internationalization, Samsung mobile was facing multiple internal and external triggers which lead them to change their internationalization strategy. Balancing scale with strategic and operational flexibility is the difficult thing for Samsung because the local brand extensions are very high in different local markets they are serving. It is merely impossible to achieve scale economy while keeping in mind strategic and operational flexibility. (Hyun et al., 2004)
• Using direct exporting strategy Samsung was facing difficulty as they required more time, energy and money to serve the global market of telecommunication. Many competitors were having significant multi domestic presence, which may serve as a limitation for Samsung to lose competitive edge in global market.
• There was a sense of urgency for Samsung to acquire more people power to cultivate a global customer base. Serving global market with direct exporting strategy demanded more responsibility from every level of organization.
• Samsung was facing multiple bottlenecks, as it was help directly accountable with no buffer zone. Beside that customers in host markets were unable to communicate and give their feedback as quickly as a local agent can.
• Samsung was facing high logistics and distribution related costs for handling warranties and transactions. Samsung was unable to provide on-site start-up training and ongoing support services.
2.2 Internal and External Triggers at “Joint Venture” Stage:
It merely impossible to maintain quality in all brands especially local brands with such a diverse portfolio, it is very difficult to strategically align with the companies in joint venture, acquisition and licensing. Social, cultural, legal and political risk event might initiate, unless pre risk assessment of alliance is done. At this stage of internationalization Samsung was facing multiple bottlenecks as competitive pressure from emerging Chinese and Japanese smartphone manufacturer. Following are internal and external triggers faced by Samsung during Joint venture stage of strategic alliance.
• Samsung was finding hard to build sustainable relationship with their strategic partners as there was imbalance level of expertise, investments brought into the venture by multiple strategic partners.
• Different cultures and management styles result in poor integration and co-operation.
• Samsung partners and strategic alliance partners didn’t provide enough leadership and support in the early stages.
2.3 Internal and External Triggers at “R&D Consortia” Stage:
Samsung went for research and development consortia for different reasons. Among the reasons cited are market pressures, international competition, the increased pace of new product development, cutbacks in corporate research and development budgets, and shared concerns about meeting new regulatory or safety requirements. Product life cycle (PLC) analysis shows the series of phases where consumers demand for product changes. Product life cycle of high tech consumer electronics is generally low as no product can be in demand for ever. Author believes that “smart phone” division of Samsung has already ended up with the maturity phase of PLC. The below figure shows the PLC for Samsung Galaxy Series (Shannon and Manley, 2013)
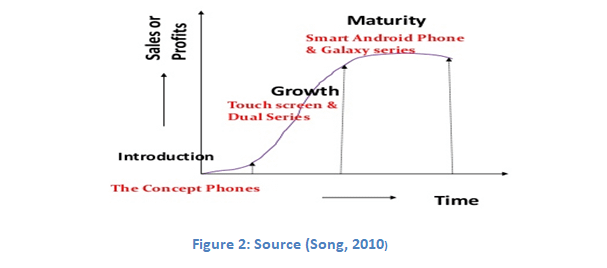
Author believes that Samsung needs to come up with new innovation, in order to survive in market, if not they will continuously witness the negative trend of sales in the upcoming quarters. (Song, 2010)
3.0 ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF STRATEGIES USED BY SAMSUNG:
3.1 Direct Export Stage:
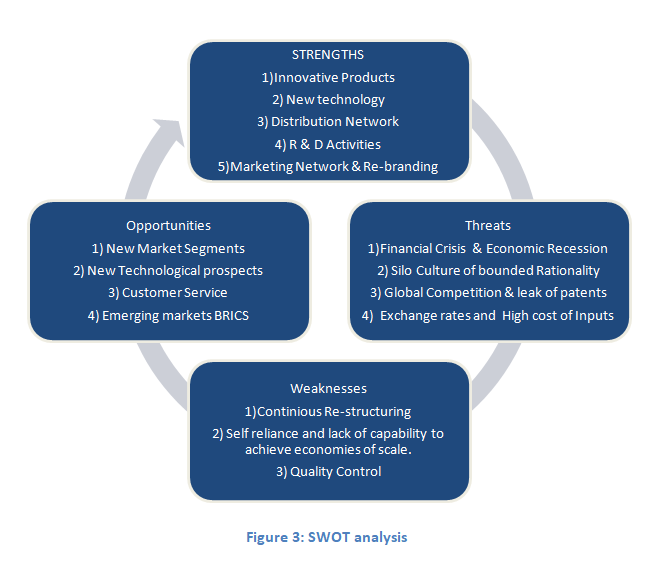
This analysis S.W.O.T analysis which includes strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and weaknesses is a famous strategic business tool used by managers to screen internal and external environment faced by the company. Analysis of these internal and external environmental factors can enable author to analyse competitive environment faced by Samsung Telecommunication division.
SWOT Analysis:
3.2 Joint Venture:
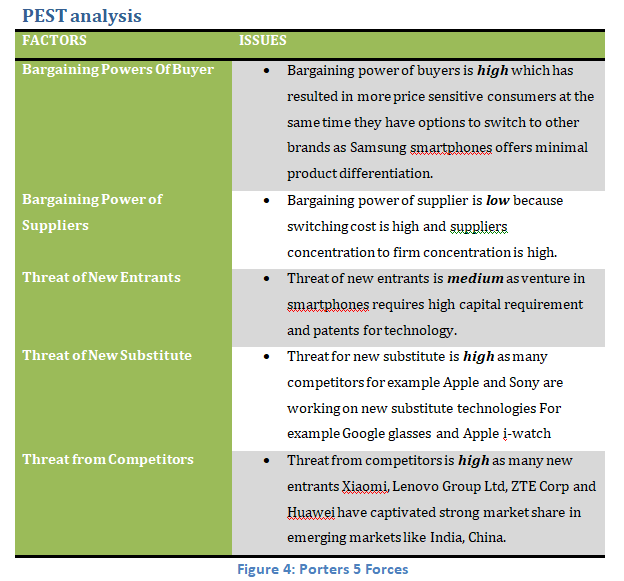
The PEST Analysis is a powerful kind of analysis that can make the external environment of the company more clear to observe and is a useful tool for understanding market growth or decline and the market`s opportunities and threats, as well as it is a business measurement tool.
3.3 R&D Consortia:
The below analysis reveals that driving forces overcomes retraining forces thus it is essential to initiate change and transform Samsung to organization which fosters new culture of innovation and creativity so they can come up with breakthrough design of smartphones and new technologies along with compatible operating system or software.
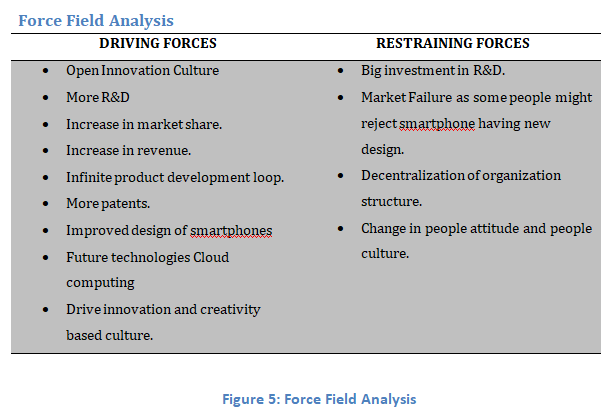
4.0 REAL LIFE OUTCOMES (SUCCESS/FAILURE) OF THE STRATEGIC INITIATIVES:
Samsung have implemented their global strategy which aims to achieve global efficiency by producing top quality products at their best costs. They focus on world-class scale manufacturing and R&D with centralized co-ordination and management. Samsung mobiles tends to expand and exploit potential scale economies at all level of their operations especially in growth markets like China, Philippines and India which has significant potential capita is increasing at phenomenal rate, company tend to shift their production plant for some brands to those markets because the cost of production was relatively low and demand was continuously increasing.
Successful Implications of Strategy:
(a) Leveraging Local Platform: Local brands and access to economic scale in distribution are key value drivers in most geographical markets.
(b) Global Brands Production: Samsung is constantly optimizing the production of their global brands like Galaxy constantly from one plant to another, since they want to produce on full capacity to reduce their fixed cost.
Negative Implications of Strategy:
(a) Managing Risks through Multinational Flexibility: Balancing scale with strategic and operational flexibility is the difficult thing for Samsung because the local brand extensions are very high in different local markets they are serving. It is merely impossible to achieve scale economy while keeping in mind strategic and operational flexibility.
(b) Investment Risks: Samsung operations and equity investments in these markets are subject to the customary risks of operating in developing countries such emerging market risks could adversely impact their cash flows.
5.0 MICHAEL PORTER’S NATIONAL DIAMOND FRAMEWORK (1990) ANALYSIS OF SAMSUNG:
In 1990 Porters proposed Diamond model which provides framework to evaluate competitive strategy and advantage of nation. Porter develops the concept, bridging the gap between strategic management and international economics. Porters suggests that national competitive advantage depends upon four determinants which includes factor costs, domestic demand, related and supported industries in the home country, and amount of rivalry in the home country between leading firms/institutions by sector. Change events (such as technological discontinuities, global shifts or political decisions by foreign governments) matter because they create discontinuities that allow shifts in competitive position (Porter, 1990).
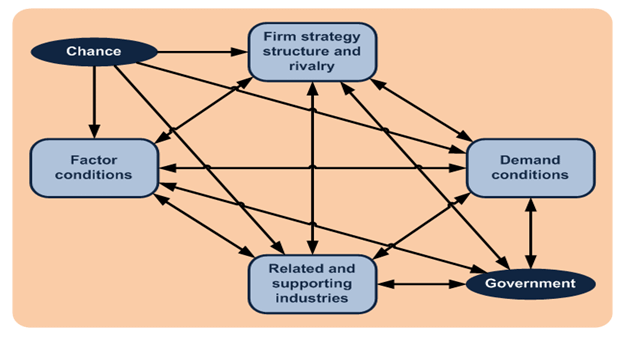
Figure 6: Porter Diamond Model
5.1 Factor Conditions for Samsung:
Samsung is leading Korean brand representing ideologies of Korea which is situated in Asia, with high proximity to China and East Asian Countries. Samsung’s main R/D facility and all its fab lines located at a single site just below Seoul. Benefit of Collocation, and scale of fab investment. Engineers live together, air is fresh, beautiful, productive environment. The overall level of education in Korea is relatively high Korean government has planned to support educational institutions such as colleges and private institutes related to IT skills and The number of programs containing higher education in computer science/engineering is increasing. Therefore the supply and the quality of Korea’s skilled workforce is expected increased.
5.2 Demand Conditions:
Korea has shown the high computing penetration rate since 1998. Korean demand for computers of Samsung at global scale, Samsung encourages the continuous development of technology and improvement of business models in business it sectors. According to Porter, home demand is determined by three major characteristics: their mixture (the mix of customers’ needs and wants), their scope and growth rate, and the mechanisms that transmit domestic preferences to foreign markets. Porter states that a country can achieve national advantages in an industry or market segment, if home demand provides clearer and earlier signals of demand trends to domestic suppliers than to foreign competitors. In Korea everything from super markets to consumer electronic has been dominated by Samsung.
5.3 Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry:
The conditions in a country that determine how companies are established, are organized and are managed, and that determine the characteristics of domestic competition. Samsung, because of the unique ecosystem created around it, has successfully spread its product line across both of these dimensions which includes competitive advantage and target market. For example Hynix Semiconductor – Local competitor, competition within Korea effect strengthened as they are both global competitors.
5.4 Related and Supported industries:
Samsung has secured leading position in DRAM market . In addition, Samsung ranks itself in top manufacture in LCD and Mobile phone. With continuous efforts to develop new technology and to reach niche market abroad, Korea can keep the leading position in the global market.
6.0 CONCLUSION:
Author has analyzed Samsung telecommunication as case in context of internationalization and global strategy. Samsung Group is Korean based company operating in consumer electronics segment established in 1969. Globalization has created opportunities for firms to extend beyond the border of their home country and operate with affiliates and branches in more than one country. As an MNC’s Samsung has significant presence in more than 69 countries and emerged as a top five largest multinational in the world. Samsung has used variety of internationalization strategy in different situational context. From direct export Samsung approach strategy to depend on local-for-local innovations, a process requiring the subsidiary to not only identify local needs but also use its own local resources to respond to those needs using joint venture strategy. Being a technology giant Samsung has recognized the importance of global R&D, Samsung has engaged in multiple R&D consortia in 8 different countries. Author have listed the internal and external triggers which enabled Samsung to review their process of internationalization and peruse for change in internationalization strategy from global to multi domestic strategy. Author has used managerial decision making tools and model such as (a) SWOT analysis, (b) Porter 5 forces and (3) force field analysis to evaluate their strategy at each distinct stage of internationalization. In the ends author has conducted Porter Diamond model analysis for Samsung telecomm manufacturer to list factor costs, domestic demand, related and supported industries in the home country, and amount of rivalry they are facing.
[ Get Superior Strategic Management Assignment Help From Expert Writers and Enjoy Amazing Grades ]
REFERENCES:
Cateora, P.R. and Ghauri, P, N.. (2000): International Marketing – European Edition. London: McGraw-Hill.
CCS Insight Report. (2014). Global Smartphone Market Analysis and Outlook: Disruption in a Changing Marke. Retrieved from http://www.lenovo.com/transactions/pdf/CCS-Insight-Smartphone-Market-Analysis-Full-Report-07-2014.pdf
Hyun, S., Han, M., and Yeh, J., (2004)“Anycall: Building a Powerful Brand,” Korea Marketing Journal Vol. 5(4),
Lee, B. Y., & Lee, S. J. (2010). Case Study of Samsung’s Mobile Phone Business. KDI School of Public Policy and Management. Retrieved from http://211.253.40.86/mille/service/PBH/10000/IMG/000000000489/W04-11.pdf
Porras., & Aymes. (2010). Korean transnational corporations: Driving force in the processes of regional integration. Retrieved from http://international.ucla.edu/media/files/Lopez_Salas-eb-xgy.pdf
Samsung Official website, (2014), retrieved from http://www.samsung.com/pk/aboutsamsung/samsungelectronics/researchdevelopment.html on 12 February, 2014.
Shanon, G., & Manley, A. (2013). Change Management in the Consumer Electronics Industry. An Interactive Qualifying Project: submitted to the faculty of Worcester Polytechnic Institute.
Song, H. C. (2010). Analysis of the global smartphone market and the strategies of its major players. University of Texas at Dallas. Retrieved from http://jgbc.fiu.edu/files/journals/2/articles/36/public/36-150-1-PB.pdf

