Title: Corporate Level Strategy of Samsung
Category: Coursework
Sub Category: Strategic Management Assignment
Subject: Strategic Management
References: APA
1.1 Company Background:
Samsung has been serving various sectors through diversified businesses for more than seventy years. It has become a digital leader because of its ability to determine the needs of the consumers before time and by continuously investing in research through its design labs. This innovation program and the talented human resource along with the collaboration of various stakeholders have led the company to achieve new levels of growth. Samsung provides products to consumers, businesses and industrial products or components to various industries. It is headquartered in Seoul, Korea. It has now become the leader in consumer electronics and is one of the most technology-driven companies in Asia. The vision of Samsung Group is “Inspire the World, Create the Future”. This vision of the company is being achieved by using its core competencies to develop new technologies for making innovative products and solutions for its customers. The focus on innovation and research has made the company achieve new levels of growth. The company’s focus on it research and development have enabled it to determine the future needs of customers before creating the relevant technology to make that product. Based on the vision statement, Samsung plans to enter into new markets by using their core competencies. Their goal is to be one of the top five brands of the world by the end of the next decade. The vision of Samsung shows that they plan to remain the market leaders in the future as well by always being the first to evaluate the upcoming needs of their customers before any of its competitors, so that they will be the one to create the future by forming relevant technologies to cater to those demands (Lee & Lee 2010).

1.2 Strategic Business Units (SBU’s):
Samsung Electronics is a global brand which owns more than 160 subsidiaries worldwide. The company has divided its operation and functions into three main divisions of consumer electronics, Information technology and mobile communications and Device solutions which are further divided into more sub divisions of Semiconductor and Display Panels (Razdan , 2017).According to Lee and Lee, (2010) Samsung Group is Korean based company operating in consumer electronics segment established in 1969. Samsung started up with the manufacturing of black and white television with joint venture with SANYO which Japanese consumer electronics manufacturer. Samsung started its mobile manufacturing in 1988 launching their first phone SH-100 for Korean market. Extensive R&D and investment in new wireless technology enabled Samsung to achieve its competitive advantage based upon the technology leadership, economies of scales, brand power, and superior negotiation power over suppliers and mobile service providers. In recent times Samsung has emerged as a largest conglomerate with more than 80 subsidiaries operating in diversified product division of construction, consumer electronics, financial services, shipbuilding, and medical services.
1.3 Corporate Level Strategy:
Scope:
Corporate level strategy of Samsung revolves around (a) vertical integration and (b) diversification. Vertical integration includes leveraging all process of manufacturing as Samsung being a smartphone manufacturer have invested in subsidiaries through acquisition to create manufacturing of electronic components used in smartphones and electronic appliances. This strategy has enabled Samsung to become the market leader in electronic appliances. One third of the revenue from electronic components comes from the competitors with whole Samsung is competing which includes Sony, Apple, Dell and Hewlet-Packard. Diversification is another corporate level strategy being used by Samsung as Samsung have more than 26 manufacturing plants around the world where it combines technology, expertise and facilities to create a synergy between all the strategic business units. For example, Samsung have diversified into businesses like textiles, retail, automobile manufacturing, petrochemicals, shipbuilding and aerospace. (Park, Alvstam, Dolles & Storm, 2011) Samsung chaebols invested into automobile production in 1994 backed by Samsung leveraged relationship of technology licensing agreement with Nissan motors. In 1998 SMI started their first production of passenger’s cars.
Corporate Parenting:
Samsung owns 34 R&D centers which have an expert staff of 50 thousand and over which include human resource talent of scientists, engineers and designers given them competitor edge over rivals (Samsung, 2017). Samsung adds value using its 34 R&D centers through groundbreaking innovation and value creation.
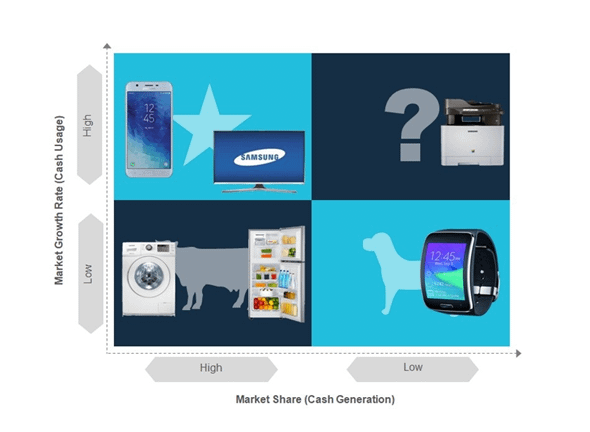
Portfolio Matrices:
Samsung should invest in consumer electronics which is the strongest SBU of Samsung accounted for highest amount of market growth and market share as showed in figure below.
[ Get Superior Strategic Management Assignment Help From Expert Writers and Enjoy Amazing Grades ]
References:
Lee, W., & Lee, N. S. (2010). Understanding Samsung’s Diversification Strategy: The Case of Samsung Motors Inc. Long Range Planning 40 (2007) 488e504.
Razdan, V. (2017). Analysis of Samsung Electronics’ Strategy for the period 2014-2017, and development of strategic options for growth.
Park, S., Alvstam, C. G., Dolles, H., & Ström, P. (2014). Samsung Electronics: From ‘National champion’ to ‘Global leader’. Asian Inward and Outward FDI, 179-200. https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137312211_9

